What is Gastroscopy?
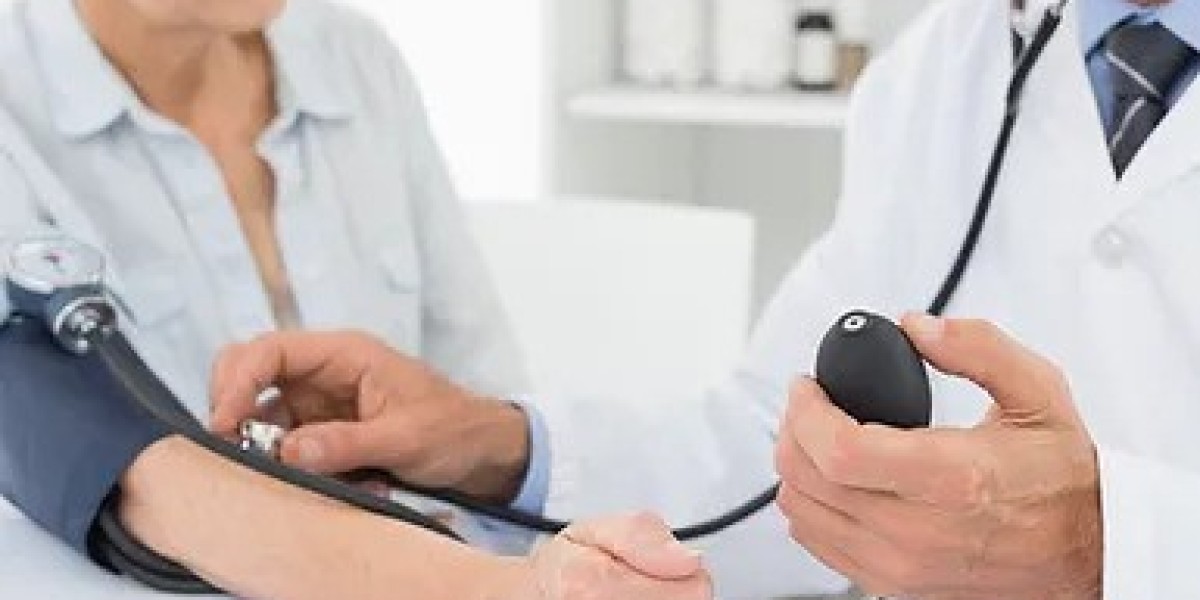
Gastroscopy, also known as Oesophago-Gastro-Duodenoscopy (OGD), is a minimally invasive procedure used to examine the lining of the upper digestive tract, including the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. In Singapore, where digestive disorders are prevalent due to dietary habits and lifestyle factors, gastroscopy plays a role in diagnosing conditions such as gastritis, ulcers, and even early-stage cancers.
Gastroscopy is performed using a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope. This instrument contains a tiny camera and light source, allowing the gastroenterologist to visualize the internal structures of the digestive tract in real-time.
How is Gastroscopy Done?
During a gastroscopy procedure, patients are typically sedated to ensure comfort and minimize discomfort. Sedation is administered intravenously or through a combination of medications, depending on the patient's medical history and preferences. A local anesthetic spray will be used to numb your throat.
Sedation helps relax the patient and reduce gag reflexes, making the procedure more tolerable.
The examination takes about 10-20 minutes to complete. You may experience mild bloating or belching as air is inflated to distend the stomach. It is a procedure that is painless, and has no effect on your breathing.
Once sedated, the gastroenterologist gently inserts the endoscope through the mouth and guides it down the esophagus into the stomach and duodenum. Throughout the procedure, the gastroenterologist carefully examines the lining of the digestive tract, looking for abnormalities such as inflammation, polyps, ulcers, or tumors. If necessary, tissue samples (biopsies) may be taken for further analysis.
Gastroscopy is commonly performed as an outpatient procedure in Singapore. Patients are usually able to resume normal activities shortly after the procedure, although they may experience some mild throat discomfort or bloating.
What are the Benefits of Gastroscopy?
Gastroscopy enables early detection and diagnosis of various gastrointestinal conditions, including ulcers, inflammation, polyps and tumors. In Singapore, where early intervention is key to managing digestive disorders effectively, gastroscopy plays a crucial role in facilitating timely diagnosis and treatment.
In addition to diagnosis, gastroscopy allows for therapeutic interventions such as the removal of polyps, control of bleeding, and dilatation of strictures. These interventions can help alleviate symptoms and improve the overall health and well-being of patients in Singapore.
Gastroscopy is also used as a screening tool for detecting early-stage cancers of the upper digestive tract, including esophageal and gastric cancers. Regular screening is particularly important where the incidence of digestive cancers remains a significant health concern.
Read more ; gastroscopy procedure singapore