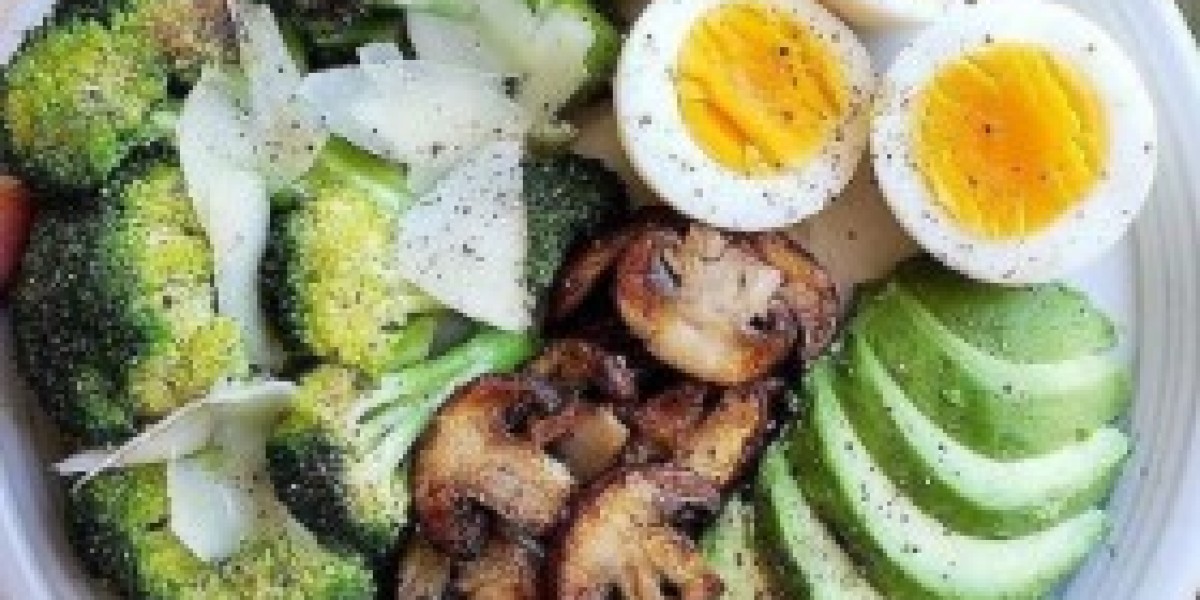
Keto Diet Plan commonly known as the keto diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan designed to induce a state of ketosis in the body. This metabolic state encourages the body to burn fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. The keto diet has gained popularity for its potential benefits, including weight loss, improved energy levels, and better blood sugar control. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at the keto diet, including its principles, meal planning, benefits, and potential challenges.
What is the Keto Diet?
Definition and Principles
Keto Diet: The ketogenic diet is a dietary regimen that emphasizes high-fat and very low-carb intake. The primary goal is to shift the body’s metabolism from using glucose (derived from carbohydrates) as its primary energy source to using ketones, which are produced from fat.
Ketosis: This is the metabolic state where the body primarily burns fat for fuel. Ketosis is achieved when carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced, prompting the liver to produce ketones from fatty acids.
Macronutrient Breakdown
- Fat: 70-75% of total daily calories
- Protein: 20-25% of total daily calories
- Carbohydrates: 5-10% of total daily calories
How the Keto Diet Works
Metabolic Pathways
Glucose vs. Ketones: Normally, the body relies on glucose for energy. In ketosis, the liver converts fatty acids into ketones, which become the primary energy source.
Insulin Levels: Reducing carbohydrate intake lowers insulin levels, which helps to stabilize blood sugar and promotes fat burning.
Achieving Ketosis
Carbohydrate Restriction: To enter and maintain ketosis, daily carbohydrate intake is generally limited to 20-50 grams of net carbs (total carbs minus fiber) per day.
Fat Intake: High-fat foods are encouraged to meet energy needs and support the ketosis process.
Keto Diet Meal Planning
1. Breakfast
Low-Carb Options:
- Eggs and Avocado: Scrambled eggs cooked in butter with sliced avocado.
- Greek Yogurt with Nuts: Unsweetened Greek yogurt topped with chia seeds, nuts, and a few berries.
- Smoothie: A keto-friendly smoothie made with spinach, coconut milk, protein powder, and a small amount of berries.
2. Lunch
Low-Carb Options:
- Salad with Protein: A mixed greens salad with grilled chicken, avocado, olive oil, and vinegar.
- Lettuce Wraps: Lettuce wraps filled with turkey, cheese, avocado, and mayo.
- Soup: Creamy cauliflower soup made with bone broth, heavy cream, and spices.
3. Dinner
Low-Carb Options:
- Grilled Salmon: Salmon fillets grilled with a side of sautéed spinach and mushrooms.
- Zucchini Noodles: Zucchini noodles with a rich meat sauce made from ground beef and low-carb vegetables.
- Chicken Alfredo: Chicken breast served with a creamy Alfredo sauce made with heavy cream and Parmesan cheese.
4. Snacks
Low-Carb Options:
- Cheese and Olives: A small serving of cheese with a handful of olives.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, or pumpkin seeds.
- Keto Bars: Store-bought or homemade low-carb protein bars.
Keto-Friendly Foods
1. Fats and Oils
Types:
- Avocado Oil: Ideal for cooking and salad dressings.
- Coconut Oil: Provides a source of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) that support ketosis.
- Butter: A staple fat for cooking and baking.
2. Proteins
Sources:
- Meat: Beef, pork, lamb, and poultry.
- Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
- Eggs: A versatile source of protein and fat.
3. Low-Carb Vegetables
Types:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and lettuce.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts.
- Others: Zucchini, bell peppers, and asparagus.
4. Dairy
Types:
- Cheese: Cheddar, mozzarella, and cream cheese.
- Heavy Cream: Used in cooking and coffee.
- Greek Yogurt: Unsweetened and full-fat varieties.
5. Beverages
Types:
- Water: Essential for hydration.
- Herbal Teas: Unsweetened and free from carbohydrates.
- Black Coffee: Low in carbs and can be consumed with a splash of heavy cream.
Benefits of the Keto Diet
1. Weight Loss
Mechanism: The keto diet promotes fat burning by shifting the body’s energy source from carbohydrates to fat.
Studies: Research shows that individuals on a keto diet often experience rapid initial weight loss and improved body composition.
2. Improved Blood Sugar Control
Mechanism: By reducing carbohydrate intake, the keto diet helps stabilize blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
Studies: Evidence suggests that the keto diet can be beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
3. Increased Energy Levels
Mechanism: Ketones provide a more stable and efficient energy source compared to glucose.
Reports: Many people on the keto diet report increased energy levels and reduced fatigue.
4. Enhanced Mental Clarity
Mechanism: Ketones are a more efficient fuel for the brain than glucose, potentially improving cognitive function.
Reports: Some individuals experience improved focus, memory, and mental clarity on the keto diet.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
1. Keto Flu
Description: Some individuals experience flu-like symptoms during the initial phase of the diet, including headache, fatigue, and nausea.
Management:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water and consider electrolyte supplements.
- Gradual Transition: Slowly reduce carbohydrate intake to ease into ketosis.
2. Nutrient Deficiencies
Risk: The restrictive nature of the keto diet may lead to deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Prevention:
- Supplementation: Consider taking a multivitamin or specific supplements to address potential deficiencies.
- Diverse Foods: Include a variety of low-carb vegetables and high-quality protein sources.
3. Long-Term Sustainability
Considerations: Maintaining the keto diet long-term can be challenging for some individuals due to its restrictive nature.
Strategies:
- Flexibility: Consider a more flexible approach or cyclical keto diet if strict adherence is difficult.
- Support: Seek support from keto communities or professional nutritionists.
4. Social and Lifestyle Adjustments
Challenges: Social gatherings and dining out can be challenging on the keto diet due to limited food options.
Solutions:
- Meal Prep: Prepare keto-friendly meals and snacks to bring along.
- Communication: Inform friends and family about your dietary needs to find suitable options.
Conclusion
The keto diet offers a unique approach to weight loss, energy management, and blood sugar control by shifting the body’s metabolism to utilize fat as its primary fuel source. While it provides numerous benefits, including improved mental clarity and enhanced energy levels, it also presents challenges such as nutrient deficiencies and social adjustments. By understanding the principles of the keto diet, planning meals carefully, and addressing potential challenges, individuals can successfully incorporate this dietary approach into their lifestyle. Whether you're new to keto or looking to refine your current plan, this comprehensive guide serves as a valuable resource for navigating and thriving on the keto diet.